Package Comparison¶
Martin Vonk - 2023
This notebooks compares the calculated drought indices to other (Python) packages or time series retrieved from other locations. Current comparisons include:
standard_precip (Python)
climate_indices (Python)
pastas (Python)
SPEI (R)
Please note that it can be difficult to install these packages. SPEI (R) requires the R library. Pastas depends on Numba which has strict requirements for NumPy. Climate Indices only supports Python 3.11 and lower. Therefore running this notebook can be cumbersome.
Future comparisons:
Required packages¶
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import scipy.stats as scs
import spei as si
print(si.show_versions())
python: 3.11.14
spei: 0.8.1
numpy: 2.3.5
scipy: 1.16.3
matplotlib: 3.10.8
pandas: 2.3.3
Read Precipitation Data¶
[2]:
df = pd.read_csv("data/DEBILT.csv", index_col=0, parse_dates=True)
df.index.name = "date"
prec = df["Prec [m/d] 260_DEBILT"].multiply(1e3).rename("rain")
head = df["Head [m] B32C0572_DEBILT"].rename("B32C0572").dropna()
_ = prec.plot(grid=True, linewidth=0.5, title="Precipitation", figsize=(6.5, 4))
[3]:
# get rolling sum
prec_rsum = prec.resample("ME").sum()
_ = prec_rsum.plot(
grid=True, linewidth=0.5, title="Precipitation, monthly sum", figsize=(6.5, 4)
)
Compute Standardized Precipitation Index¶
Using SPEI package¶
[4]:
spi = si.spi(prec_rsum, dist=scs.gamma, prob_zero=True, timescale=3, fit_freq="ME")
spi # pandas Series
[4]:
date
1959-09-30 -0.859224
1959-10-31 -1.897037
1959-11-30 -2.189269
1959-12-31 -1.000515
1960-01-31 -0.231999
...
2025-01-31 0.272794
2025-02-28 -0.152606
2025-03-31 -1.156964
2025-04-30 -1.394517
2025-05-31 -2.469426
Freq: ME, Length: 789, dtype: float64
Using standard_precip package¶
[5]:
from standard_precip import spi as sp_spi
# standard_precip also needs rolling sum dataframe, even though you provide freq="M" and scale = 1
precdf = prec_rsum.to_frame().reset_index().copy()
# initialize spi
standardp_spi_inst = sp_spi.SPI()
# caclulate index with many parameters
standardp_spi = standardp_spi_inst.calculate(
precdf,
date_col="date",
precip_cols="rain",
freq="M",
scale=3, # note that scale is not the same for the standard deviation in SciPy
fit_type="mle",
dist_type="gam",
)
standardp_spi.index = standardp_spi.loc[
:, "date"
].values # create datetimeindex because date had to be a column
standardp_spi # pandas DataFrame
[5]:
| date | rain_scale_3 | rain_scale_3_calculated_index | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1959-07-31 | 1959-07-31 | NaN | NaN |
| 1959-08-31 | 1959-08-31 | NaN | NaN |
| 1959-09-30 | 1959-09-30 | 79.1 | -1.977699 |
| 1959-10-31 | 1959-10-31 | 102.0 | -1.953337 |
| 1959-11-30 | 1959-11-30 | 110.8 | -2.189269 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2025-01-31 | 2025-01-31 | 253.0 | 0.288813 |
| 2025-02-28 | 2025-02-28 | 201.2 | -0.118100 |
| 2025-03-31 | 2025-03-31 | 121.8 | -1.157576 |
| 2025-04-30 | 2025-04-30 | 72.2 | -1.723688 |
| 2025-05-31 | 2025-05-31 | 39.2 | -2.480334 |
791 rows × 3 columns
Using climate_indices package¶
Previously there was a significant difference beteween the SPEI and climate_indices package, not sure why. I thought it had something to do with the fitting method used for the gamma distribution. In issue #61 it was mentioned that the same outcome could be achieved. However, I found it difficult to install climate_indces due to lack of support (for newer python versions).
[6]:
# from climate_indices.compute import scale_values, Periodicity
# from climate_indices import compute, indices, utils
[7]:
# initial_year = prec_rsum.index[0].year
# calibration_year_initial = prec_rsum.index[0].year
# calibration_year_final = prec_rsum.index[-1].year
# period_times = 366
# scale = 1
# periodicity = compute.Periodicity.daily
# values = prec_rsum.values
# scaled_values = compute.scale_values(
# values,
# scale=scale,
# periodicity=periodicity,
# )
# alphas, betas = compute.gamma_parameters(
# scaled_values,
# data_start_year=initial_year,
# calibration_start_year=calibration_year_initial,
# calibration_end_year=calibration_year_final,
# periodicity=periodicity,
# )
# gamma_params = {"alpha": alphas, "beta": betas}
# spival = indices.spi(
# values,
# scale=scale,
# distribution=indices.Distribution.gamma,
# data_start_year=initial_year,
# calibration_year_initial=calibration_year_initial,
# calibration_year_final=calibration_year_final,
# periodicity=compute.Periodicity.daily,
# fitting_params=gamma_params,
# )
# climateind_spi = pd.Series(spival, index=prec_rsum.index, name="Climate Index SPI")
# climateind_spi
Using SPEI R package¶
[8]:
from rpy2.robjects import pandas2ri
from rpy2.robjects.packages import importr
sr = importr("SPEI")
with pandas2ri.converter.context(): # pandas2ri.activate()
spir_res = sr.spi(prec_rsum.values, scale=3)
r_spi = pd.Series(spir_res[2].ravel(), index=prec_rsum.index, name="SPI")
r_spi
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
PackageNotInstalledError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[8], line 4
1 from rpy2.robjects import pandas2ri
2 from rpy2.robjects.packages import importr
----> 4 sr = importr("SPEI")
6 with pandas2ri.converter.context(): # pandas2ri.activate()
7 spir_res = sr.spi(prec_rsum.values, scale=3)
File ~/work/SPEI/SPEI/.tox/docu/lib/python3.11/site-packages/rpy2/robjects/packages.py:472, in importr(name, lib_loc, robject_translations, signature_translation, suppress_messages, on_conflict, symbol_r2python, symbol_resolve, data)
440 """ Import an R package.
441
442 Arguments:
(...) 468
469 """
471 if not isinstalled(name, lib_loc=lib_loc):
--> 472 raise PackageNotInstalledError(
473 'The R package "%s" is not installed.' % name
474 )
476 if suppress_messages:
477 ok = quiet_require(name, lib_loc=lib_loc)
PackageNotInstalledError: The R package "SPEI" is not installed.
Plot and compare¶
[9]:
f, ax = plt.subplot_mosaic(
[["SPI"], ["DIFF"]],
figsize=(8, 4),
sharex=True,
height_ratios=[2, 1],
)
spi.plot(ax=ax["SPI"], grid=True, linestyle="-", label="SPI")
standardp_spi.iloc[:, -1].plot(
ax=ax["SPI"],
color="C1",
grid=True,
linestyle="--",
label="standard_precip",
)
# climateind_spi.plot(
# ax=ax["SPI"], color="C2", grid=True, linestyle=":", label="climate_indices"
# )
# r_spi.plot(ax=ax["SPI"], color="C2", grid=True, linestyle=":", label="R package")
(ax["SPI"].set_ylim(-3.5, 3.5),)
(ax["SPI"].set_title("Comparison"),)
(ax["SPI"].set_ylabel("SPI"),)
ax["SPI"].legend(ncol=3)
(spi - standardp_spi.iloc[:, -1]).plot(
ax=ax["DIFF"], color="C4", label="SPEI - standard_precip", grid=True
)
# (spi - r_spi).plot(ax=ax["DIFF"], color="C3", label="SPEI - R Package")
# ax["DIFF1"].set_ylim(-0.05, 0.05)
ax["DIFF"].legend(ncol=2)
ax["DIFF"].set_title("SPEI minus other package")
ax["DIFF"].set_ylabel("Difference")
ax["DIFF"].set_xlim("1996", "1999")
f.tight_layout()
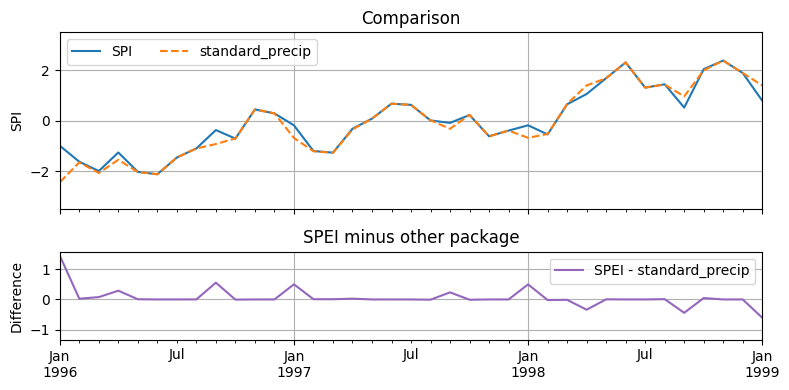
Difference is very small between SPEI an the standard_precip package.
The standard_precip package does not explicitely support the Standardized Precipitation Evaporation Index, as far as I can see. However, the SPI class in standard_precip could probably be used, even though the naming of precip_cols is not universal. In general, the standard_precip package needs much more keyword arguments while the SPEI package makes more use of all the nice logic already available in SciPy and Pandas.
The climate_indices package needs even more code.
The SPEI R package also has a similar result but seems to vary a bit more. More research is needed to understand why that is the case. Most likely is the differences in fitting the gamma distribution.
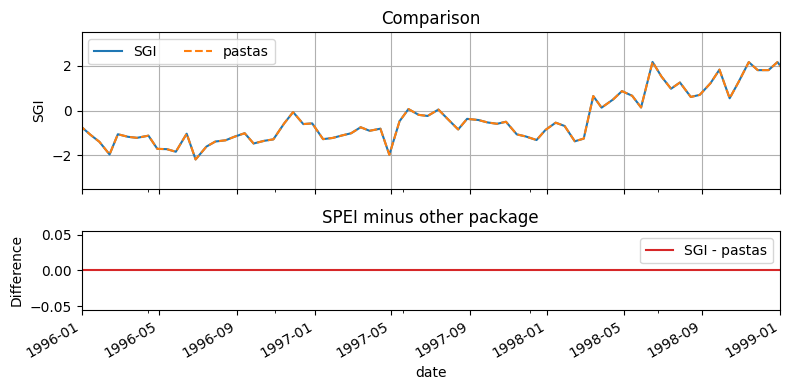
Compute Standardized Groundwater Index¶
[10]:
import pastas as ps
sgi = si.sgi(head, fit_freq="ME")
sgi_pastas = ps.stats.sgi(head)
[11]:
pd.concat([sgi, sgi_pastas], axis=1).rename(columns={0: "SGI", "head": "Pastas"})
[11]:
| SGI | B32C0572 | |
|---|---|---|
| date | ||
| 1968-12-13 | 0.510073 | 0.510073 |
| 1968-12-24 | 0.398855 | 0.398855 |
| 1969-01-14 | 0.220807 | 0.220807 |
| 1969-01-28 | 0.744936 | 0.744936 |
| 1969-02-14 | 0.650837 | 0.650837 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 2020-10-28 | -0.052796 | -0.052796 |
| 2020-11-15 | -0.628006 | -0.628006 |
| 2020-11-27 | -0.510073 | -0.510073 |
| 2020-12-14 | -0.823894 | -0.823894 |
| 2020-12-28 | 0.345126 | 0.345126 |
1225 rows × 2 columns
[12]:
f, ax = plt.subplot_mosaic(
[["SGI"], ["DIFF"]],
figsize=(8, 4),
sharex=True,
height_ratios=[2, 1],
)
sgi.plot(ax=ax["SGI"], grid=True, linestyle="-", label="SGI")
sgi_pastas.plot(ax=ax["SGI"], color="C1", grid=True, linestyle="--", label="pastas")
(ax["SGI"].set_ylim(-3.5, 3.5),)
(ax["SGI"].set_title("Comparison"),)
(ax["SGI"].set_ylabel("SGI"),)
ax["SGI"].legend(ncol=3)
(sgi - sgi_pastas).plot(ax=ax["DIFF"], color="C3", label="SGI - pastas")
ax["DIFF"].legend(ncol=2)
ax["DIFF"].set_title("SPEI minus other package")
ax["DIFF"].set_ylabel("Difference")
ax["DIFF"].set_xlim("1996", "1999")
f.tight_layout()