Drought Prediction with Time Series Modeling¶
Martin Vonk - 2022
This notebooks shows a quick calculation of the SPI, SPEI and SGI for De Bilt, in the Netherlands. The SGI is calculated using a Pastas time series model since the original time series is too short. The application of time series models for extrapolating groundwater time series is discussed in Brakkee et al (2022).
Required packages¶
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import pastas as ps
import scipy.stats as scs
import spei as si # si for standardized index
print(si.show_versions())
python: 3.11.14
spei: 0.8.1
numpy: 2.3.5
scipy: 1.16.3
matplotlib: 3.10.8
pandas: 2.3.3
Import time series¶
Time series are imported using the package hydropandas. Enddate is by default yesterday. The head time series is obtained from a Pastas test dataset.
[2]:
# import hydropandas as hpd
# today = datetime.date.today()
# yesterday = (today - datetime.timedelta(days=1)).strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
# prec = (
# hpd.PrecipitationObs.from_knmi(
# meteo_var="RH", stn=260, startdate="1959-07-01", enddate=yesterday
# )
# .multiply(1e3)
# .squeeze()
# )
# prec.index = prec.index.normalize()
# evap = (
# hpd.EvaporationObs.from_knmi(
# meteo_var="EV24", stn=260, startdate="1959-07-01", enddate=yesterday
# )
# .multiply(1e3)
# .squeeze()
# )
# evap.index = evap.index.normalize()
df = pd.read_csv("data/DEBILT.csv", index_col=0, parse_dates=True)
prec = df["Prec [m/d] 260_DEBILT"].multiply(1e3).rename("prec")
evap = df["Evap [m/d] 260_DEBILT"].multiply(1e3).rename("evap")
head = df["Head [m] B32C0572_DEBILT"].rename("B32C0572").dropna()
today = df.index[-1]
yesterday = df.index[-2]
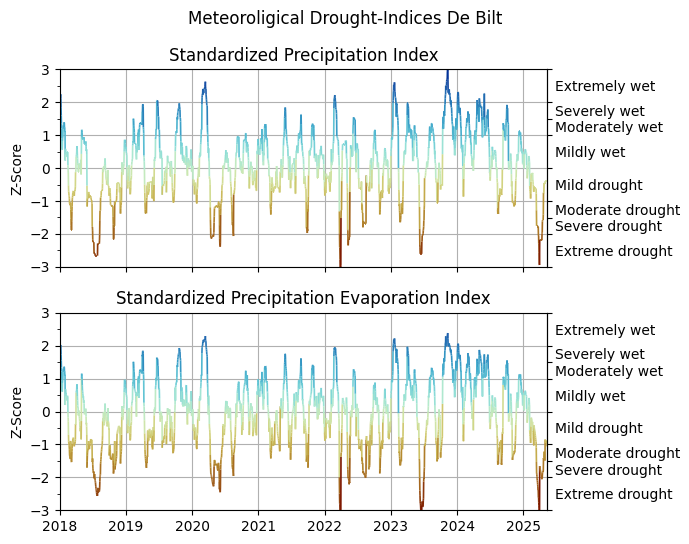
Calculate SPI and SPEI¶
[3]:
# Accumulate time series on monthly basis
spi1 = si.spi(prec, timescale=30, dist=scs.gamma, fit_freq="MS")
spei1 = si.spei((prec - evap), timescale=30, dist=scs.fisk, fit_freq="MS")
[4]:
xlim = pd.to_datetime(["2018-01-01", df.index[-1]])
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(7.0, 5.5), sharex=True)
si.plot.si(spi1, ax=axs[0], background=False, cmap="roma")
si.plot.si(spei1, ax=axs[1], background=False, cmap="roma")
[(x.grid(), x.set_xlim(xlim), x.set_ylabel("Z-Score")) for x in axs]
axs[0].set_title("Standardized Precipitation Index")
axs[1].set_title("Standardized Precipitation Evaporation Index")
fig.suptitle("Meteoroligical Drought-Indices De Bilt")
fig.tight_layout()
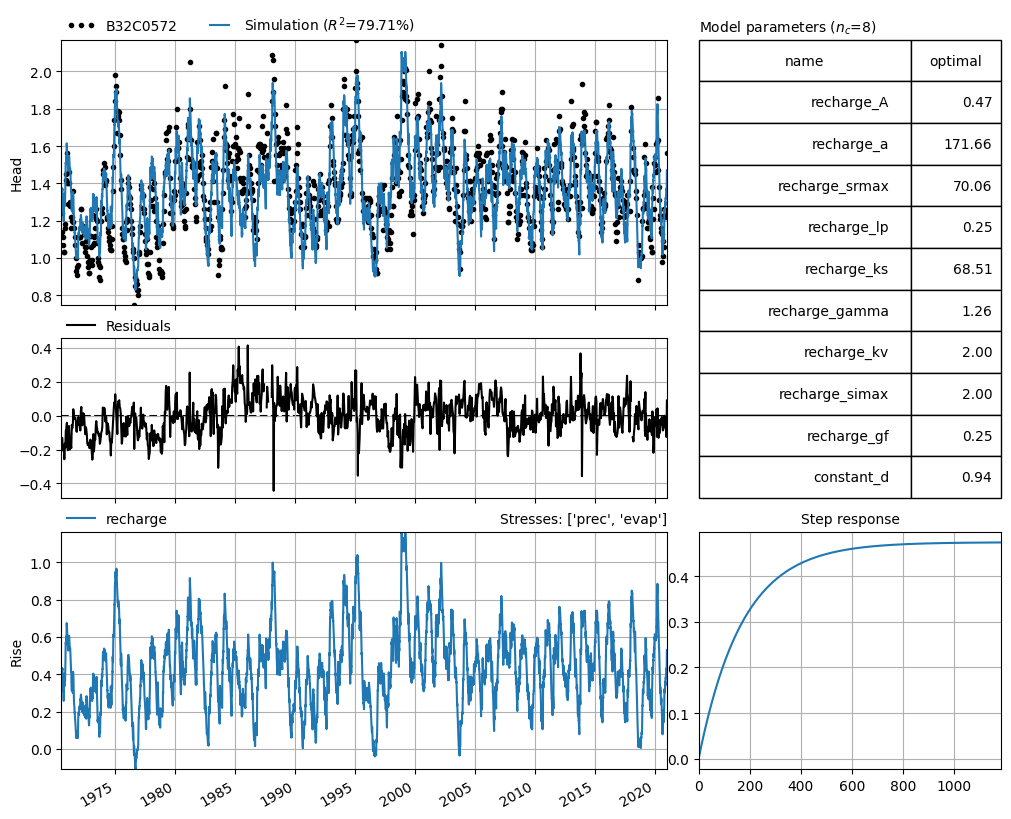
Create time series model and simulate head¶
[5]:
ml = ps.Model(head)
rm = ps.RechargeModel(
prec, evap, ps.Exponential(), recharge=ps.rch.FlexModel(gw_uptake=True)
)
ml.add_stressmodel(rm)
ml.solve(tmin="1970-07-01", report=True)
_ = ml.plots.results(figsize=(10.0, 8.0))
Fit report B32C0572 Fit Statistics
==================================================
nfev 45 EVP 79.61
nobs 1187 R2 0.80
noise False RMSE 0.11
tmin 1970-07-01 00:00:00 AICc -5305.21
tmax 2020-12-28 00:00:00 BIC -5264.70
freq D Obj 6.71
freq_obs None ___
warmup 3650 days 00:00:00 Interp. No
solver LeastSquares weights Yes
Parameters (8 optimized)
==================================================
optimal initial vary
recharge_A 0.468697 0.443936 True
recharge_a 170.731185 10.000000 True
recharge_srmax 103.744124 250.000000 True
recharge_lp 0.250000 0.250000 False
recharge_ks 145.327844 100.000000 True
recharge_gamma 1.470452 2.000000 True
recharge_kv 1.999723 1.000000 True
recharge_simax 2.000000 2.000000 False
recharge_gf 0.250354 1.000000 True
constant_d 0.950055 1.377665 True
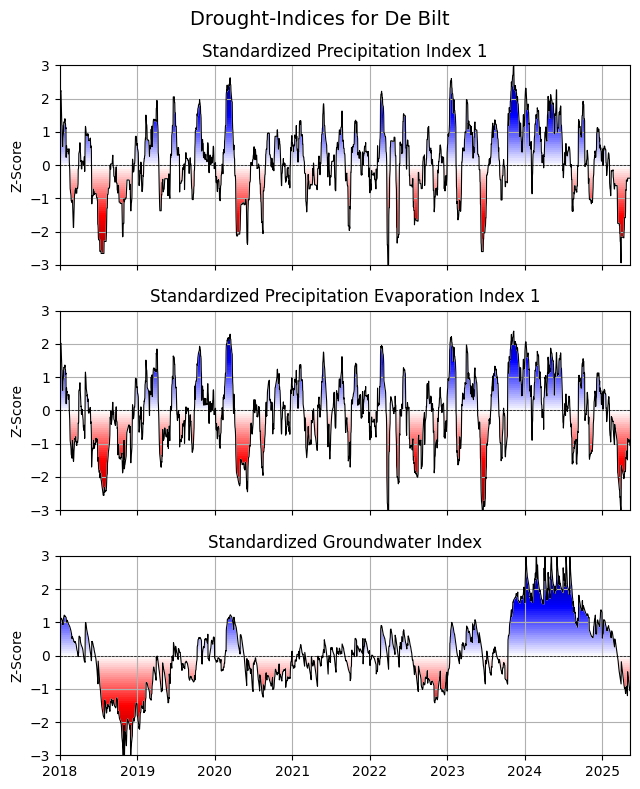
Calculate SGI based on time series model¶
[6]:
gws = ml.simulate(tmin="1990-07-01", tmax=yesterday)
sgi = si.sgi(gws, fit_freq="MS")
Compare three drought-indices (SPI, SPEI, SGI) in plot¶
[7]:
fig, axs = plt.subplot_mosaic(
[["SPI"], ["SPEI"], ["SGI"]], figsize=(6.5, 8), sharex=True
)
si.plot.si(spi1, ax=axs["SPI"], add_category=False)
si.plot.si(spei1, ax=axs["SPEI"], add_category=False)
si.plot.si(sgi, ax=axs["SGI"], add_category=False)
[(axs[x].grid(), axs[x].set(xlim=xlim, ylabel="Z-Score")) for x in axs]
axs["SPI"].set_title("Standardized Precipitation Index 1")
axs["SPEI"].set_title("Standardized Precipitation Evaporation Index 1")
axs["SGI"].set_title("Standardized Groundwater Index")
fig.suptitle("Drought-Indices for De Bilt", fontsize=14)
fig.tight_layout()
# fig.savefig('Drought_Index_Bilt.png', dpi=600, bbox_inches='tight')
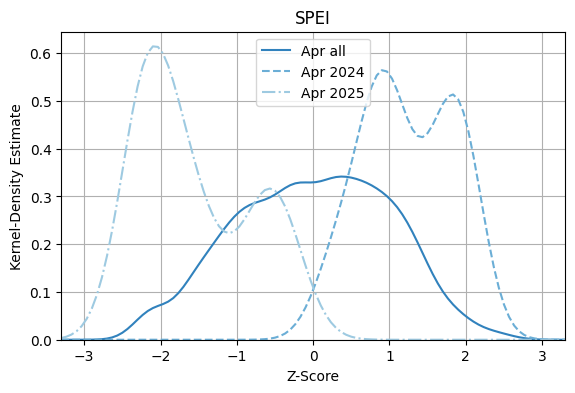
Compare SPEI Kernel Density Estimate for one month¶
[8]:
ax = si.plot.monthly_density(
spi1, years=[today.year - 1, today.year], months=[today.month - 1]
)
ax.set_xlabel("Z-Score")
ax.set_title("SPEI");